The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is intensifying its efforts to reclaim control over the eastern region, which has been plagued by insurgency. The government has announced a $5 million bounty for information leading to the capture of three high-profile rebel leaders who have played a key role in the ongoing conflict.

Who Are the Wanted Leaders?
Corneille Nangaa, a former head of the DRC’s electoral commission, now leads the Congo River Alliance, a coalition that includes the notorious M23 rebel group. Under his leadership, M23 has taken control of significant portions of eastern DRC, staging large rallies in occupied cities. Alongside him, the Congolese government has placed a bounty on two other key M23 figures: Sultani Makenga and Bertrand Bisimwa.
These three individuals were convicted in absentia last year by a military tribunal and sentenced to death for treason. Despite the ruling, they continue to operate freely, posing a serious threat to national stability.
Bounty on Journalists and Other Alleged Accomplices
In an unprecedented move, the DRC government has also placed a $4 million bounty on two exiled journalists and other individuals it considers accomplices. This has raised concerns over press freedom and the targeting of opposition voices under the guise of national security.
Challenges in Arresting Rebel Leaders
Although the bounty signals the government’s determination, capturing these fugitives remains an uphill battle. The Congolese military has struggled to match the strength of the Rwandan-backed M23 rebels, who have seized vast territories, including key cities like Goma and Bukavu. The rebel advances have displaced hundreds of thousands, leaving them without shelter or access to basic necessities.
International Pressure and Rwanda’s Role in the Conflict
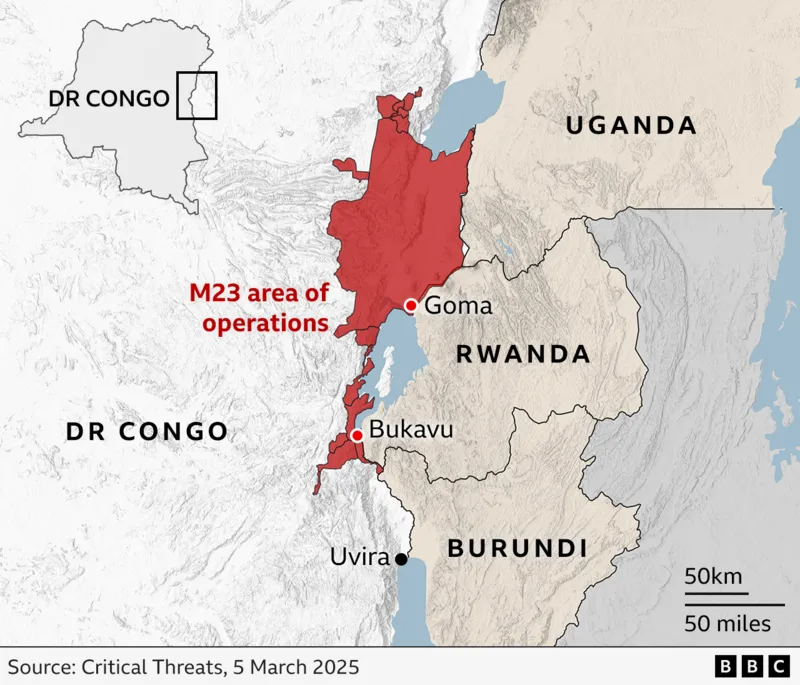
As military efforts stall, President Félix Tshisekedi is focusing on diplomatic strategies, urging the international community to impose sanctions on Rwanda for its alleged support of M23. A UN report last year confirmed that up to 4,000 Rwandan troops were operating alongside M23 rebels inside the DRC.
The Congolese government accuses Rwanda of attempting to seize its valuable mineral resources, including gold and coltan—essential components in mobile phones and computers. In response, President Tshisekedi has invited the United States to directly source these materials from the DRC rather than from Rwanda, which he accuses of smuggling looted minerals across the border.
Rwanda’s Stance and the Ethnic Dimension
While Rwanda denies mineral exploitation, it no longer refutes allegations of supporting M23. However, it claims this involvement is aimed at preventing the conflict from spilling into its own territory. Additionally, Rwanda accuses the DRC of collaborating with the Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Rwanda (FDLR), an armed group linked to the perpetrators of the 1994 Rwandan genocide.
This ethnic and political dynamic further complicates the crisis, as both M23 and the Rwandan government are led by members of the Tutsi ethnic group. The Congolese government, on the other hand, denies any cooperation with the FDLR.
What Lies Ahead?
With diplomatic negotiations stalling and military operations facing setbacks, the DRC’s latest strategy—placing hefty bounties on rebel leaders—remains uncertain in its effectiveness. However, as international scrutiny intensifies, the outcome of this conflict will largely depend on regional cooperation, global intervention, and a decisive shift in military strategy.
The crisis in eastern DRC is far from over, and its resolution will have profound implications for regional stability, economic development, and humanitarian efforts.




